Robotic Surgery
Urological robotic surgery, also known as robotic-assisted surgery, is a type of minimally invasive surgery that uses a robotic system to assist the surgeon in performing urologic procedures. The robotic system, which is controlled by the surgeon, allows for greater precision, flexibility, and control during the surgery.
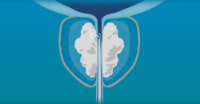
One of the most common uses of robotic surgery in urology is for the treatment of prostate cancer. The robotic system, which is known as the da Vinci surgical system, is used to perform a procedure called a robotic prostatectomy. This procedure involves the removal of the prostate gland and some surrounding tissue. Because the surgery is minimally invasive, it typically results in less blood loss and a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.
Robotic surgery is also used to treat other urologic conditions such as kidney cancer, bladder cancer, and ureteropelvic junction obstruction. It has also been used in ureteral reconstruction, pyeloplasty, and nephrectomy.
The benefits of robotic-assisted surgery include increased precision and control, smaller incisions, less blood loss, and a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. However, it's important to note that not all patients are candidates for robotic surgery, and the decision to use this type of surgery will be based on the patient's individual condition and the surgeon's experience and expertise.