Female Medicine Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
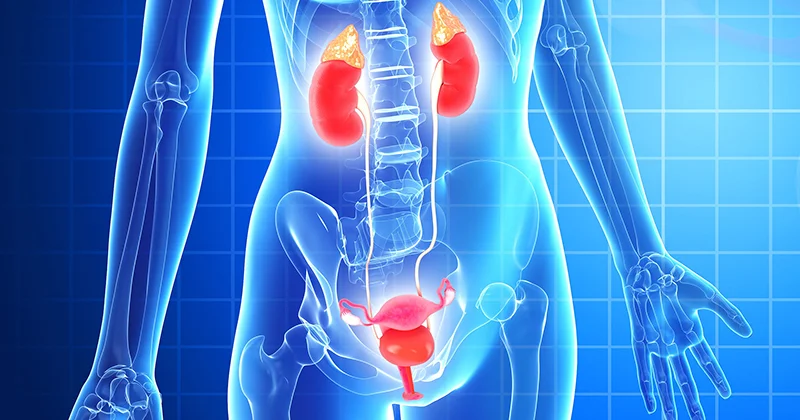
Pelvic floor reconstruction is a surgical procedure that is used to repair and strengthen the muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue of the pelvic floor in women. The pelvic floor is the group of muscles and tissues that support the bladder, uterus, and rectum, and these structures may become weakened or damaged due to various conditions such as childbirth, pelvic surgery, chronic constipation, and aging.
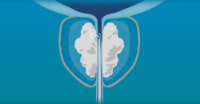
The most common condition that requires pelvic floor reconstruction is pelvic organ prolapse (POP), which is a condition where the pelvic organs such as the bladder, uterus or rectum protrude into or out of the vagina. This may cause a variety of symptoms such as pelvic pressure, discomfort, incontinence, and difficulty with sexual intercourse.
There are different types of pelvic floor reconstruction procedures, including:
- Vaginal vault suspension, which is used to support the top of the vagina and uterus
- Sacrospinous ligament fixation, which is used to support the back of the vagina
- Rectocele repair, which is used to repair a bulging of the rectum into the vagina
- Cystocele repair, which is used to repair a bulging of the bladder into the vagina
The type of procedure will depend on the specific condition and anatomy of the patient. Pelvic floor reconstruction surgery is typically done under general anesthesia and it's usually performed as an outpatient procedure. Recovery time can vary depending on the specific procedure and patients can return to normal activities in a few weeks.
It's important to note that pelvic floor reconstruction is not always the best option for all patients, and it should be considered after thorough evaluation and counseling by the healthcare professional. In some cases, non-surgical treatment options may be more appropriate.