MRI Fusion Biospy
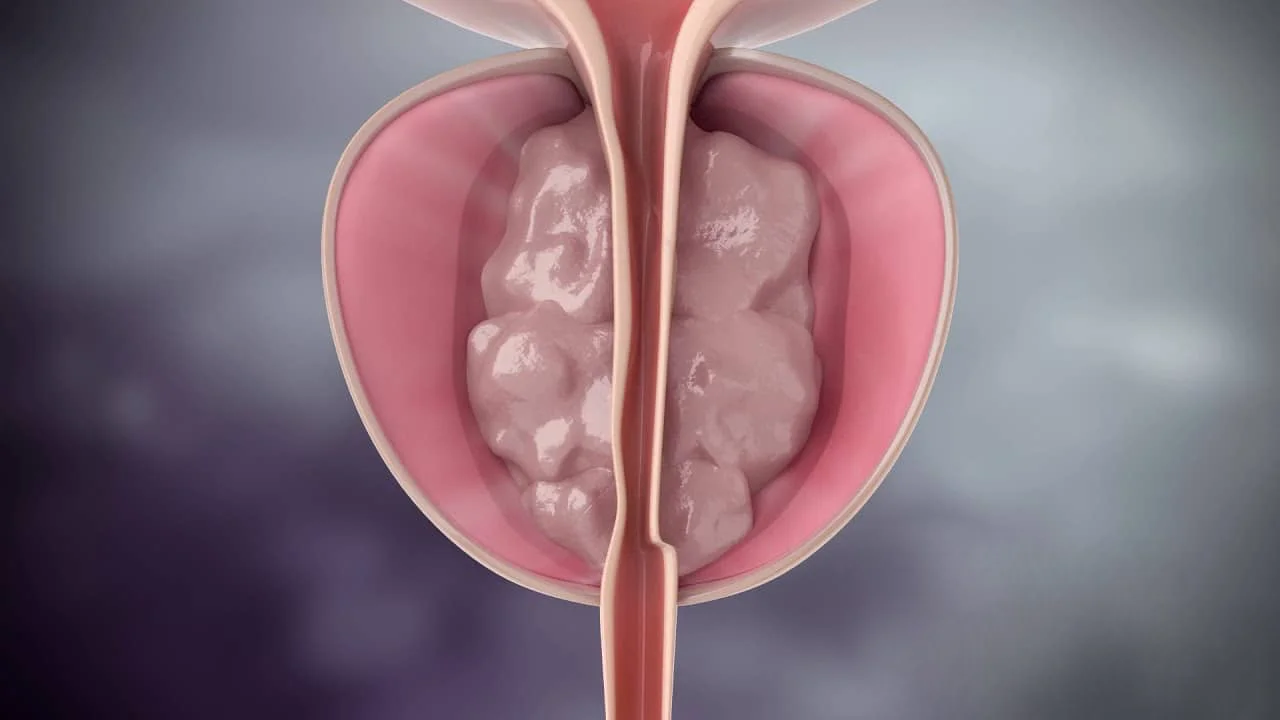
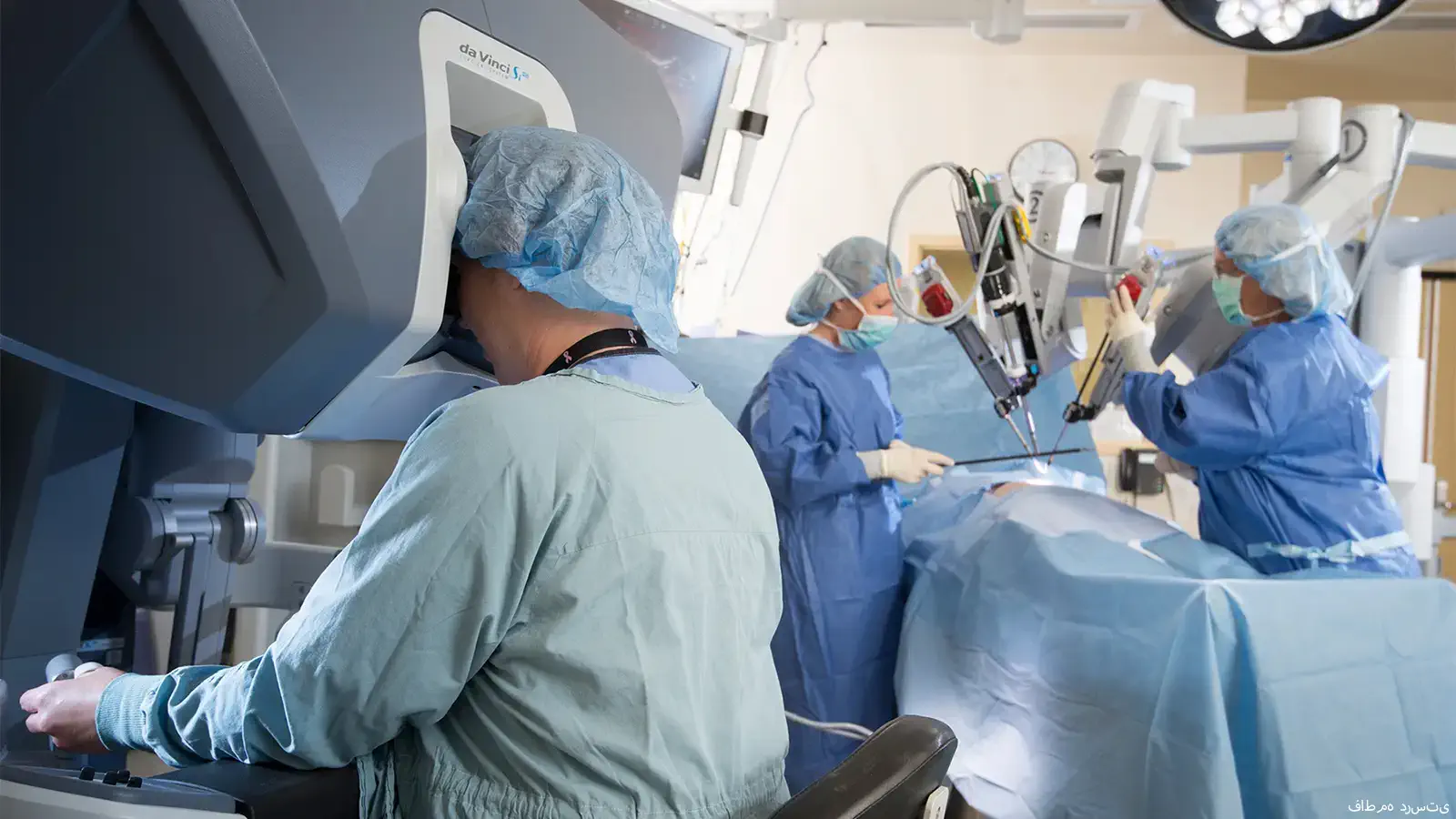
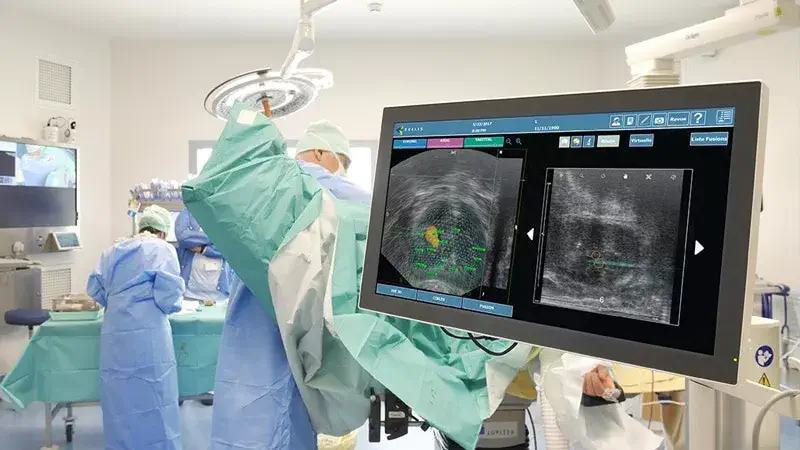
MRI Fusion Biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that combines magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with real-time ultrasound to guide the biopsy of the prostate. It is used to detect prostate cancer and other abnormalities in the prostate.
The procedure starts with an MRI scan of the prostate, which is used to create detailed images of the gland. These images are then used to identify any suspicious areas that may require a biopsy. Once the suspicious area has been identified, the patient is positioned for a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) biopsy. The TRUS probe, which is a small wand-like device, is inserted into the rectum and used to take samples of tissue from the prostate.
The procedure is usually performed as an outpatient procedure and usually takes about an hour to complete. The patient will be given a mild sedative to help them relax during the procedure. Before the procedure, the patient should inform the doctor of any medications they are taking and any allergies they have.
After the procedure, the patient may experience some discomfort or mild pain in the lower abdomen, and may be given antibiotics to prevent infection. The patient will be given instructions on how to care for themselves after the procedure, including when to return for follow-up. The results of the biopsy will be analyzed by a pathologist, and the patient will be informed of the results.
It's important to note that, while MRI Fusion biopsy is a more accurate method of detecting prostate cancer than traditional biopsy methods, it's also more expensive, and not all centers have this technology available. Patients should discuss the benefits and risks of the procedure with their doctor, as well as any specific preparation instructions.